Timing Calibration Efforts in Cosmic Ray Veto for Mu2e Experiment
Payton Beeler
Westminster College
Physics & Chemistry Major
Mentored by Dr. Tim Bolton and Dr. Glenn Horton-Smith
Timing calibration in the counters of the cosmic ray veto can help lead to increased efficiency and overall better results. This project aims to use a chi-squared analysis on simulated oscilloscope data to pinpoint the location of a cosmic ray within the counter. This can then be used to distinguish cosmic rays from background noise within the counter.
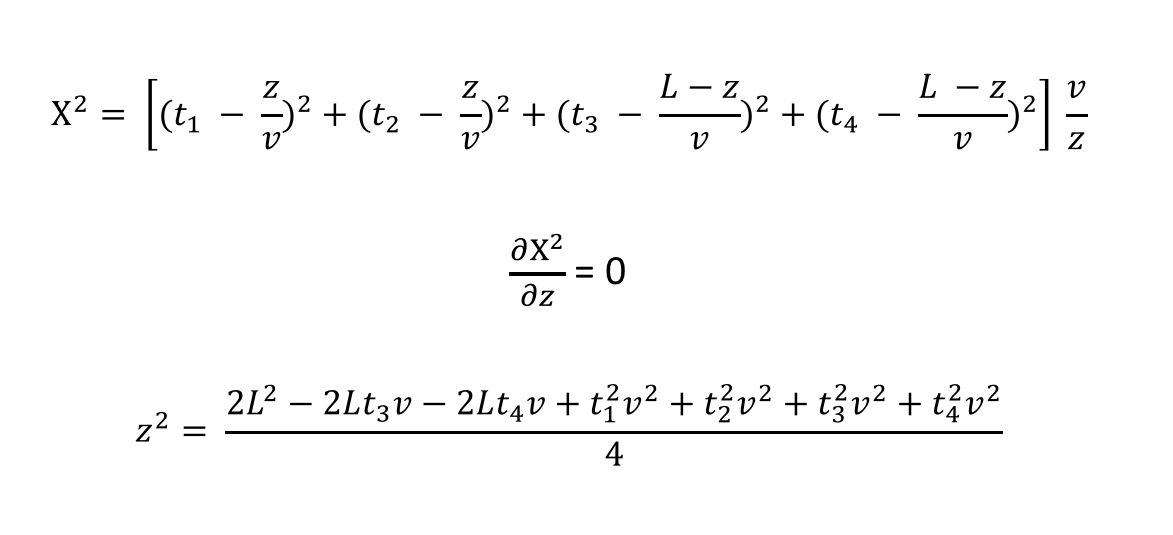
Fig. 1: Chi-squared test, minimize and solve for z to get reconstructed position from time measurements.
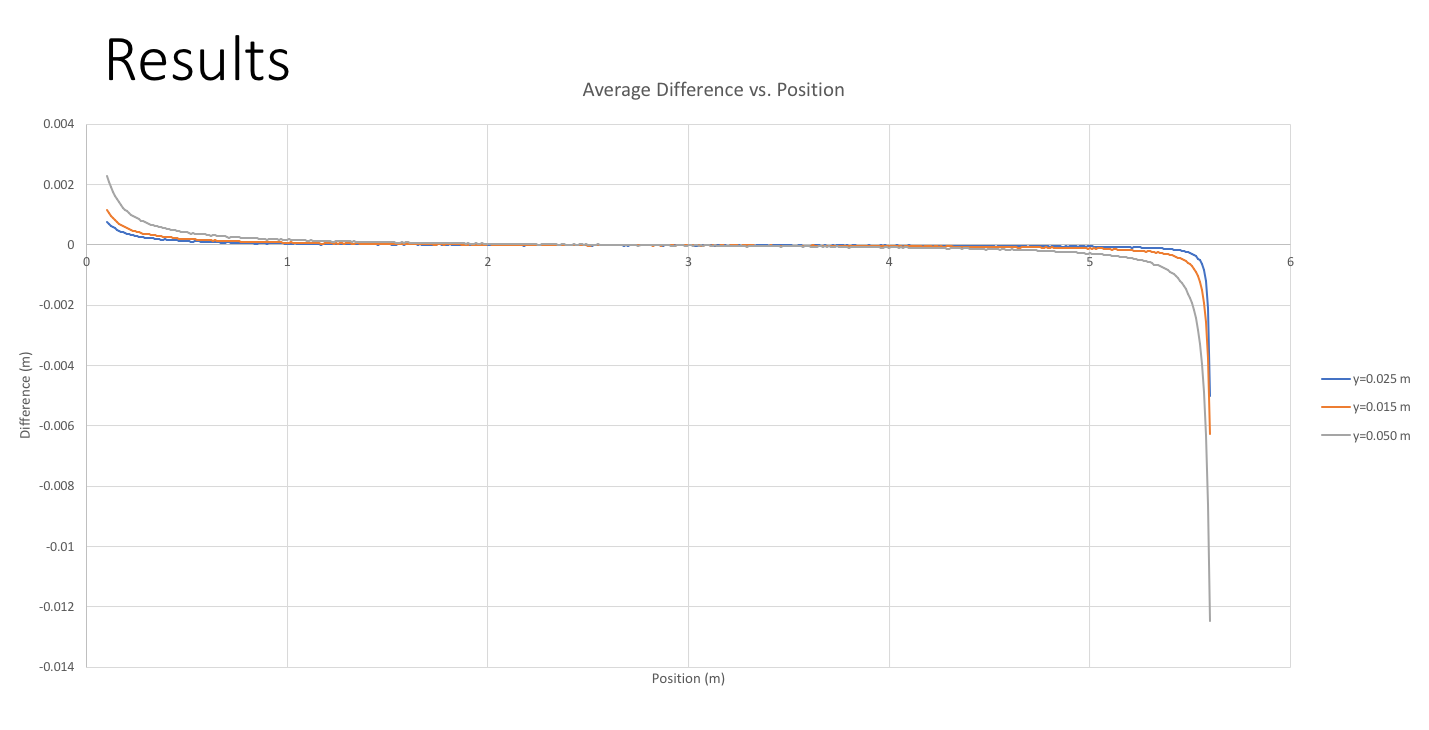
Fig. 2: Difference between actual and reconstructed positions.
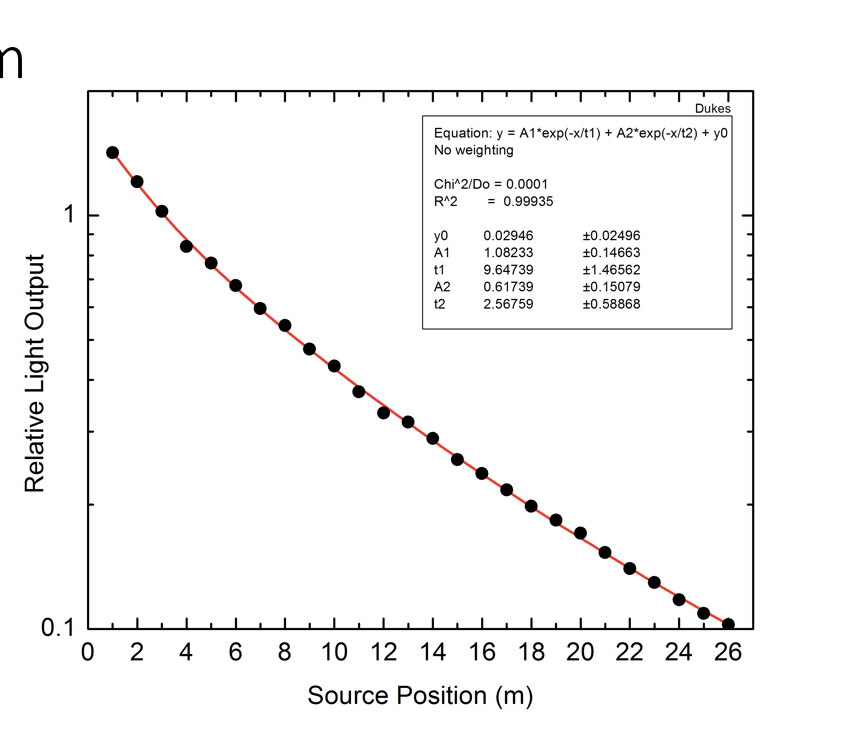
Fig. 3: Relative light output from attenuation in polystyrene which related to amplitude of signal.
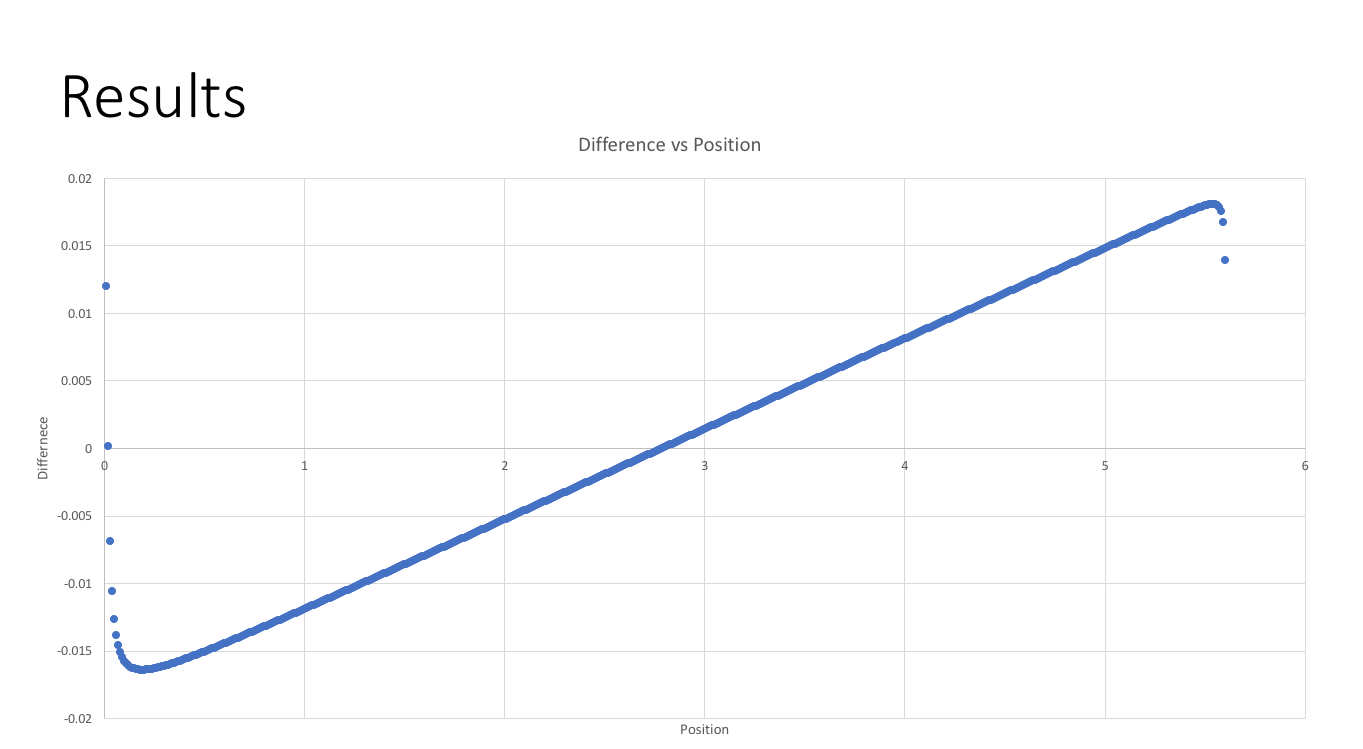
Fig. 4: Difference between actual and reconstructed positions using modified error assignment.
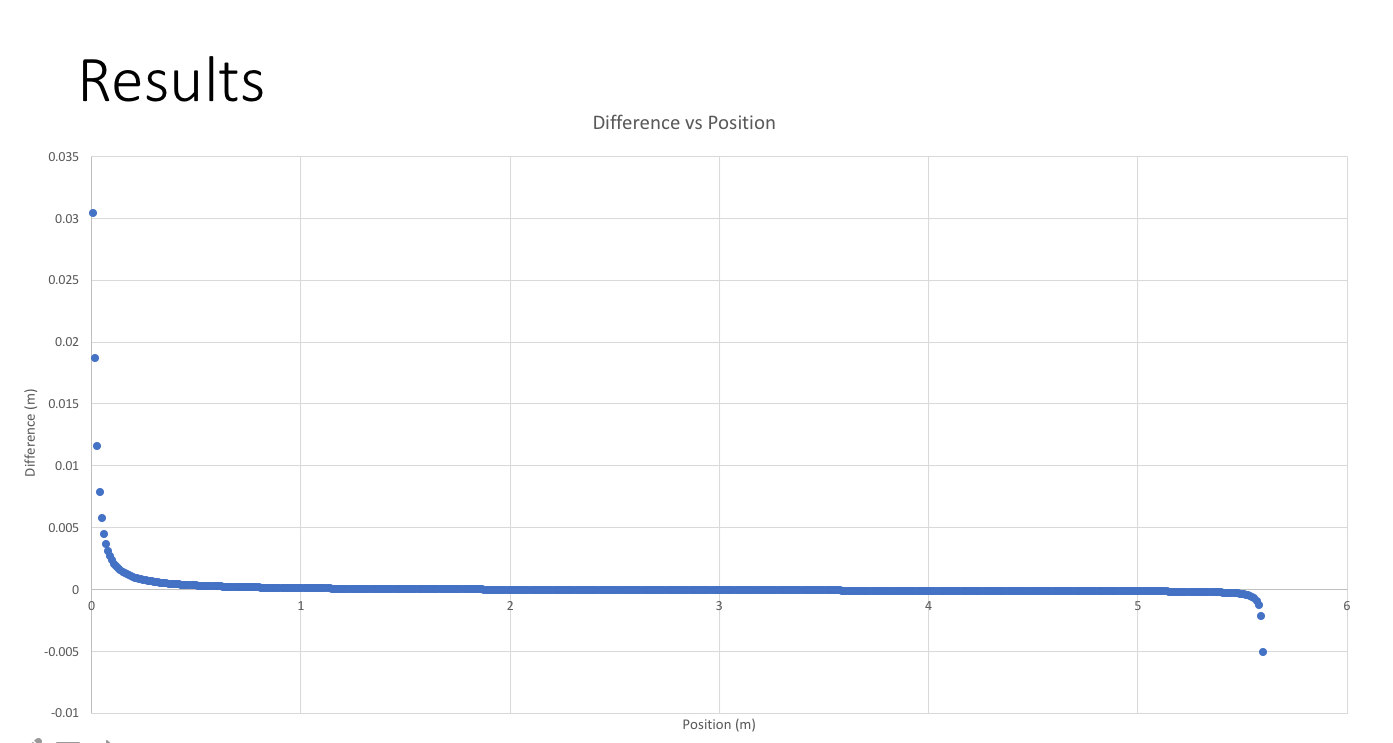
Fig. 5: Difference between actual and reconstructed positions accounting for systematic error.